National
India's First Solar Mission, Aditya L1
⇒ ISRO’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV-XL) launched India’s first Solar Mission – Aditya L1 from Sathish Dhawan Space Centre SHAR (SDSC SHAR), Sriharikota on 02 September 2023.
- The 44.4 metre tall PSLV-C57 rocket with a lift off mass of 321 ton carried the spacecraft Aditya-L1 to study the Sun.
» Aditya L1 is the first space-based observatory class Indian solar mission to study the Sun. Aditya-L1 is named after the Sun God in Hindu mythology.
Plan:
- The spacecraft was planned to be placed in a halo orbit around the Lagrangian point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system, which is about 1.5 million km from the Earth.
- A satellite placed in the halo orbit around the L1 point has the major advantage of continuously viewing the Sun without any occultation/eclipses. This will provide a greater advantage of observing the solar activities and its effect on space weather in real time.
- The Aditya L1 Mission is expected to provide the most crucial information to understand the problem of coronal heating, coronal mass ejection, pre-flare and flare activities and their characteristics, dynamics of space weather, propagation of particles and fields etc.
Halo Orbit insertion:
» The Halo Orbit insertion (HOI) of Aditya L1 was achieved at approximately 4:00 PM 06 January 2024. The final phase of maneuver involved firing of control engines for a short duration.
- The orbit of Aditya L1 spacecraft is located roughly 1.5 million Kilometres from earth on a continuously moving Sun – Earth line, with an orbital period of about 177.86 earth days.
- The specific halo orbit is selected to ensure a mission lifetime of 5 years, minimizing station keeping maneuvers and thus fuel consumption and ensuring a continuous, unobstructed view of the sun.
- The halo orbit insertion of the spacecraft presented a critical mission phase, which demanded precise navigation and control.
- The spacecraft underwent a cruise phase lasting approximately 110 days to reach the halo orbit.
The success of this insertion not only signifies ISRO’s capabilities in such complex orbital maneuvers, but it gives confidence to handle future interplanetary missions.
Aditya L1 Spacecraft Payload:
The spacecraft carried seven payloads to observe the photosphere, chromosphere and the outermost layers of the Sun (the corona) using electromagnetic and particle and magnetic field detectors.
- Using the special vantage point L1, four payloads directly view the Sun and the remaining three payloads carry out in-situ studies of particles and fields at the Lagrange point L1; thus, providing important scientific studies of the propagatory effect of solar dynamics in the interplanetary medium.
Developed by:
The payloads onboard Aditya L1 were developed by Indian scientific laboratories, Indian Institute of Astrophysics, Bangalore (IIA), Inter University Centre for Astronomy & Astrophysics, Pune and ISRO.
Payloads:
- The Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) studies the solar corona and dynamics of Coronal Mass Ejections.
- The Solar Ultra-violet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) payload images the Solar Photosphere and Chromosphere in near Ultra-violet (UV) and also measures the solar irradiance variations in near UV.
- The Aditya Solar wind Particle EXperiment (ASPEX) and Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA) payloads study the solar wind and energetic ions, as well as their energy distribution.
- The Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS) and The High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS) studies the X-ray flares from the Sun over a wide X-ray energy range.
- The Magnetometer payload is capable of measuring interplanetary magnetic fields at the L1 point.
» Aditya L1 was designed and realized at UR Rao Satellite Centre (URSC) with participation from various ISRO centers.
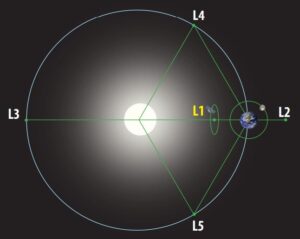
Lagrange Points:
For a two-body gravitational system, the Lagrange Points are the positions in space where a small object tends to stay, if put there. These points in space for a two body systems such as Sun and Earth can be used by spacecraft to remain at these positions with reduced fuel consumption.
- Technically at Lagrange point, the gravitational pull of the two large bodies equals the necessary centripetal force required for a small object to move with them.
- For two body gravitational systems, there are total five Lagrange points denoted as L1, L2, L3, L4 and L5.
- The Lagrange point L1 lies between Sun-Earth line. The distance of L1 from Earth is approximately 1% of the Earth-Sun distance.
The Lagrange points for Sun-Earth system are shown in the figure.
ISRO’s Aditya L1 Mission: View Pdf (Official Link)
System based automatic ‘Status Holder’ certificates under FTP 2023
⇒ In a meeting with the Export Promotion Councils on 09 October 2023, the Union Commerce & Industry Minister Shri Piyush Goyal unveiled a significant initiative to issue system based automatic ‘Status Holder’ certificates under the Foreign Trade Policy (FTP) 2023.
- Now the exporter will not be required to apply to the office of Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) for a Status Certificate.
- The export recognition will be provided by the IT system based on available Directorate General of Commercial Intelligence and Statistics (DGCIS) merchandise export electronic data and other risk parameters.
» This perspective is a paradigm shift in doing things as it not only reduces compliance burden and promotes ease of doing business but also recognizes the need and importance of collaboration within the Government.
At present, the exporter is required to file an online application along with an export certificate from a Chartered Accountant for grant of Status.
- The DGFT Regional Offices, as per the laid down timelines are supposed to issue the certificate in 3 days.
- The new arrangement will lead to a simplified regime where no applications are invited from exporters and the certification is granted every year in August based on annual export figures available with the partner government agency i.e. DGCIS.
Status Holder certification program:
- The Status Holder certification program provides credibility to the Indian exporters in the international markets.
- In addition, it provides certain other privileges including simplified procedures under FTP 2023 and priority custom clearances on self-declaration basis, exemption from compulsory negotiation of documents through banks, exemption from filing Bank Guarantee for FTP schemes etc.
International
Launch of Strategic Partnership between India and Tanzania
⇒ At the invitation of Smt Droupadi Murmu, President of the Republic of India, Her Excellency Samia Suluhu Hassan, President of the United Republic of Tanzania undertook a State Visit to the Republic of India from 8-10 October 2023.
- President Samia Suluhu Hassan was accompanied by a high-level delegation including the Minister for Foreign Affairs and East African Cooperation Hon January Makamba (MP), and other members.
Discussions:
President Samia Suluhu Hassan and Prime Minister Narendra Modi held official bilateral talks in a warm and cordial atmosphere and exchanged views on bilateral, regional and international issues of mutual interest. The President of India Smt Droupadi Murmu also held bilateral talks.
During the visit, MoUs covering a wide range of sectors were signed.
The MoUs are:
- Memorandum of Understanding between the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology of the Republic of India and the Ministry of Information, Communication and Information Technology of the United Republic of Tanzania on cooperation in the field of sharing successful digital solutions implemented at population scale for digital transformation
- Technical Agreement between The Indian Navy of the Republic of India and Tanzania Shipping Agencies Corporation of the United Republic of Tanzania on Sharing White Shipping Information
- Cultural Exchange Programme between the Government of the Republic of India and the Government of the United Republic of Tanzania for the Years 2023-2027
- Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) between National Sports Council of Tanzania and Sports Authority of India on cooperation in the field of sports
- MoU between Jawaharlal Nehru Port Authority under Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways of the Republic of India and Tanzania Investment Centre of the United Republic of Tanzania for setting up of an Industrial Park in Tanzania
- MoU between Cochin Shipyard Ltd and Marine Services Co Ltd on Cooperation in Maritime Industry
Joint Statement Highlight:
- Both sides encouraged cooperation on the Indo-Pacific noting that the AU vision for peace and security in Africa with focus on development of Blue/ocean economy for accelerated economic growth coincides with SAGAR vision.
- Both sides agreed to continue with high-level political dialogue through the Joint Commission mechanism at the Foreign Ministers’ level and bilateral meetings between Leaders. Both sides agreed to initiate a Policy Planning Dialogue between their Foreign Ministries.
- Both leaders looked forward to increased interoperability between their Armed Forces.
- India and Tanzania agreed to cooperate under the framework of the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) to ensure a peaceful, prosperous and sustainable Indian Ocean Region.
- The two sides expressed commitment to increase bilateral trade volumes and towards this end, directed the respective Officials to explore new areas of trade. It was further agreed that both sides should harmonise trade volume data and take initiatives to further enhance bilateral trade volumes by organizing visits of business delegations, business exhibitions and interaction with business communities.
- The Tanzanian side acknowledged that India is amongst the top five investment sources for Tanzania whereby 630 investment projects worth USD 3.74 billion have been registered and thus creating 60,000 new jobs. Both sides agreed to explore the possibility of setting up of an Investment Park in Tanzania, Tanzanian side assured full support in this regard.
- The two leaders expressed desire to expand bilateral trade using Local currencies. They noted that Reserve Bank of India (Indian Central Bank) has cleared the way for trade using local currencies i.e. Indian Rupee (INR) & Tanzanian Shilling by allowing the authorized banks in India to open Special Rupee Vostro Accounts (SRVA) of correspondent banks of Tanzania and that transactions using this mechanism have already materialised. The two sides agreed to continue with the consultations in order to address any concerns so as to ensure sustainability of this arrangement.
- Both sides recognised that agriculture sector cooperation remains a strong pillar in the relations whereby 98% of product lines from Tanzania are imported tariff-free using India’s Duty Free Tariff Preference (DFTP) scheme. India remains a major destination for Tanzanian cashew nuts, pigeon peas, spices, avocado and other agricultural commodities. Both sides agreed to further revitalise cooperation in this sector.
- The Tanzanian side appreciated that the Indian scholarship and capacity building program has tremendously contributed to its Human Resource development. India offers 450 Indian Technical and Economic Cooperation (ITEC) scholarships for capacity building and 70 Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) scholarships for long term programmes in 2023-24. The Indian side announced the decision to increase the number of Long term scholarships (ICCR) from 70 to 85 for the year 2023-24. As part of its commitment to the Global South, India also announced 1000 additional ITEC slots for Tanzania to be used over a 5-year period in new and emergent fields like Smart Ports, Space, Biotechnology, Artificial Intelligence, Aviation Management, etc.
- The Indian side offered collaboration in areas of space technologies and digital public infrastructure under India Stack including Unified Payments Interface (UPI) and Digital Unique Identity (Aadhar).
- Tanzania commended the decision by India to set up two ICT Centres at Dar es Salaam Institute of Technology and at Nelson Mandela African Institute for Science & Technology (NMAIST) in Arusha. Tanzanian side also express its appreciation to India for upgrading the ICT centre in NM-AIST.
- Both sides agreed to heighten cooperation in cultural exchanges and appreciated the signing of the Cultural Exchange Program for the 2023-27 periods.
- The leaders agreed to a closer collaboration between Universities and Think Tanks of the two countries.
- India and Tanzania agreed on the need for reform of the United Nations Security Council through expansion in both categories of membership. Indian side conveyed appreciation to Tanzania for its support during India’s term as a non-Permanent member of the UNSC for the period 2021-22 and also for Tanzania’s support for the Indian candidature for a non-Permanent membership of UNSC in 2028-29.
