National
The Digital Personal Data Protection Bill, 2023
⇒ Parliament passed the Digital Personal Data Protection Bill, 2023 during the Monsoon Session of Parliament in August 2023.
The Bill became an Act after the assent of the President on August 11, 2023, and is called the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023.
- This is an Act to provide for the processing of digital personal data in a manner that recognises both the right of individuals to protect their personal data and the need to process such personal data for lawful purposes and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
Salient Features of the Digital Personal Data Protection Bill, 2023:
The Bill protects digital personal data (that is, the data by which a person may be identified) by providing for the following:
- The obligations of Data Fiduciaries (that is, persons, companies and government entities who process data) for data processing (that is, collection, storage or any other operation on personal data);
- The rights and duties of Data Principals (that is, the person to whom the data relates); and
- Financial penalties for breach of rights, duties and obligations.
The Bill also seeks to achieve the following:
- Introduce data protection law with minimum disruption while ensuring necessary change in the way Data Fiduciaries process data;
- Enhance the Ease of Living and the Ease of Doing Business; and
- Enable India’s digital economy and its innovation ecosystem.
2. The Bill is based on the following seven principles:
- The principle of consented, lawful and transparent use of personal data;
- The principle of purpose limitation (use of personal data only for the purpose specified at the time of obtaining consent of the Data Principal);
- The principle of data minimisation (collection of only as much personal data as is necessary to serve the specified purpose);
- The principle of data accuracy (ensuring data is correct and updated);
- The principle of storage limitation (storing data only till it is needed for the specified purpose);
- The principle of reasonable security safeguards; and
- The principle of accountability (through adjudication of data breaches and breaches of the provisions of the Bill and imposition of penalties for the breaches).
3. The Bill has few other innovative features:
The Bill is concise and SARAL, that is, Simple, Accessible, Rational &Actionable Law as it—
- Uses plain language;
- Contains illustrations that make the meaning clear;
- Contains no provisos (“Provided that…”); and
- Has minimal cross-referencing.
4. By using the word “she” instead of “he”, for the first time it acknowledges women in Parliamentary law-making.
5. The Bill provides for following rights to the individuals:
- The right to access information about personal data processed;
- The right to correction and erasure of data;
- The right to grievance redressal; and
- The right to nominate a person to exercise rights in case of death or incapacity.
For enforcing his/her rights, an affected Data Principal may approach the Data Fiduciary in the first instance. In case he/she is not satisfied, he/she can complain against the Data Fiduciary to the Data Protection Board in a hassle-free manner.
6. The Bill provides for following obligations on the data fiduciary:
- To have security safeguards to prevent personal data breach;
- To intimate personal data breaches to the affected Data Principal and the Data Protection Board;
- To erase personal data when it is no longer needed for the specified purpose;
- To erase personal data upon withdrawal of consent;
- To have in place grievance redressal system and an officer to respond to queries from Data Principals; and
- To fulfill certain additional obligations in respect of Data Fiduciaries notified as Significant Data Fiduciaries, such as appointing a data auditor and conducting periodic Data Protection Impact Assessment to ensure higher degree of data protection.
7. The Bill safeguards the personal data of children also.
- The Bill allows a Data Fiduciary to process the personal data of children only with parental consent.
- The Bill does not permit processing which is detrimental to well-being of children or involves their tracking, behavioural monitoring or targeted advertising.
8. The exemptions provided in the Bill are as follows:
- For notified agencies, in the interest of security, sovereignty, public order, etc.;
- For research, archiving or statistical purposes;
- For startups or other notified categories of Data Fiduciaries;
- To enforce legal rights and claims;
- To perform judicial or regulatory functions;
- To prevent, detect, investigate or prosecute offences;
- To process in India personal data of non-residents under foreign contract;
- For approved merger, demerger etc.; and
- To locate defaulters and their financial assets etc.
9. The key functions of the Board are as under:
- To give directions for remediating or mitigating data breaches;
- To inquire into data breaches and complaints and impose financial penalties;
- To refer complaints for Alternate Dispute Resolution and to accept Voluntary Undertakings from Data Fiduciaries; and
- To advise the Government to block the website, app etc. of a Data Fiduciary who is found to repeatedly breach the provisions of the Bill.
India’s Chandrayaan Mission
⇒ India created history with the successful soft landing of Chandrayaan 3 on the surface of the Moon in the South Pole area on August 23, 2023.
- Chandrayaan-3 spacecraft was successfully launched onboard LVM-3 on 14th July, 2023 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, SHAR.
About Chandrayaan 3
- Chandrayaan 3, a follow-on mission to Chandrayaan-2, is an ISRO mission with the primary objective of putting a lander and rover in the highlands near the south pole of the Moon and demonstrating end-toend landing and roving capabilities. It will also make several scientific measurements on the lunar surface and from orbit. It comprises a lander/rover and a propulsion module.
- The lander/rover is similar to the Vikram rover on Chandrayaan 2, with improvements to help ensure a safe landing. The propulsion module carries the lander and rover configuration. The propulsion module/communications relay satellite remained in lunar orbit to enable communications with Earth.
- Chandrayaan-3 components included various electronic and mechanical subsystems intended to ensure safe and soft landing such as Navigation sensors, propulsion systems, guidance & control among others. Additionally, there were mechanism for release of Rover, two-way communication related antennas and other onboard electronics.
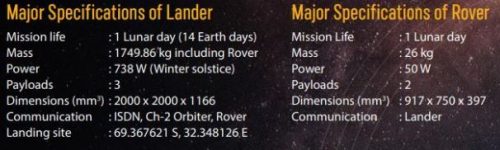
- Chandrayaan-3 Lift off mass was nearly 3896 kg and the mission life of Lander and Rover was approximately one Lunar Day which is equivalent to 14 earth days. The planned landing site for lander was ~ 690S, South Pole.
Specifications of Lander and Rover of Chandrayaan 3:
The objectives of Chandrayaan-3 were:
- To demonstrate a Safe and Soft Landing on Lunar Surface
- To demonstrate Rover exploring the moon’s surface, and
- To conduct in-situ scientific experiments.
About Chandrayaan 1:
» Chandrayaan 1 was an Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) mission designed to orbit the Moon over two years with the objectives of upgrading and testing India’s technological capabilities in space and returning scientific information on the lunar surface.
- The spacecraft launched on a PSLV C11 (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle) from the Satish Dhawan Space Center in Sriharikota on the southeast coast of India on October 22, 2008.
- The Indian Space Research Organization announced on August 31 that the Chandrayaan 1 mission has been officially terminated after contact was lost abruptly at 20:00 UT on August 28, 2009.
About Chandrayaan 2:
» Chandrayaan 2 was launched on July 22, 2019 from Satish Dhawan Space Center, Sriharikota on a GSLV Mark III.
- The primary objective of Chandrayaan 2 was to demonstrate the ability to soft-land on the lunar surface and operate a robotic rover on the surface. Scientific goals include studies of lunar topography, mineralogy, elemental abundance, the lunar exosphere, and signatures of hydroxyl and water ice.
- Contact was lost during the lander’s descent at an altitude of about 2.1 km. The lander crashed on the surface and remained in one piece, but communications and operations were impossible.
- The rover was to be deployed using a ramp shortly after landing. The lander and rover portions of the mission were planned for 14-15 days, one period of lunar daylight. The orbiter was designed for a mission life of one year but continues to operate.
International
13th BRICS Trade Ministers’ Meeting
⇒ Union Minister of Commerce and Industry, Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution and Textiles, Shri Piyush Goyal attended the 13th BRICS Trade Ministers’ Meeting held under the BRICS Presidency of South Africa virtually on 07 August 2023.
Theme:
The theme of 2023 BRICS was “BRICS and Africa: Partnership for Mutually Accelerated Growth, Sustainable Development and Inclusive Multilateralism”.
Highlights:
- Shri Piyush Goyal, touched upon issues related to WTO, Supply chain, Digitalisation, MSMEs and on the issue of Mispricing and under-invoicing in the meeting.
- The Minister lauded the South African Presidency on having an ambitious Agenda and successfully completing outcome-oriented activities under the Contact Group on Economic and Trade Issues (CGETI). He extended strong support to BRICS spirit of equality, openness, inclusiveness, consensus, mutual respect and understanding.
» BRICS is a grouping of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa.
Important Day
Indian Cost Accounts Service Day, 2023
⇒ The Indian Cost Accounts Service (ICoAS) Day was celebrated by the Office of Chief Adviser Cost, Department of Expenditure, Ministry of Finance on 09 August 2023.
Background:
- The first Indian Cost Accounts Service (ICoAS) Day was celebrated on 9th August 2015.
- The day is observed as a day to re-dedicate and re-commit ourselves to the service of the nation.
- The celebration of service day not only provides a unique opportunity for introspection as well as chalking out future strategies to deal with the challenges during the present era butalsobring esprit de corps among the ICOAS family.
